[자료구조] 이진 힙, 바이너리 힙 (Binary Heap) 이란?
2021. 10. 17. 01:56알아두면 좋을 것들
- key, value 쌍을 딕셔너리 value, 혹은 딕셔너리 페어라고도 한다.
- 아래의 글에선, 노드와 엔트리를 같은 의미로 썼다.
- 아래의 글은, Min heap을 기반으로 썼다. (Max heap이라고 큰 차이가 있는 건 아니다. 단지 heap-order property가 다를 뿐)
- heap-order property를 충족하게 힙을 고치는 것을 heapify라고도 한다.
의미/특징
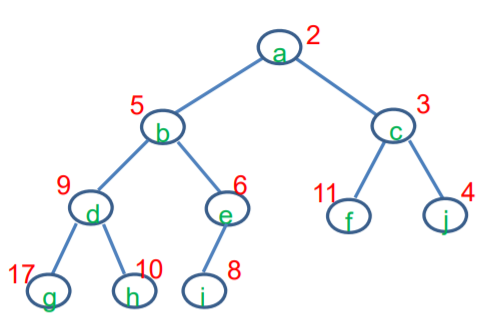
- 바이너리 힙은 힙(Heap)의 종류 중 하나.
- 바이너리 힙은 자식이 무조건 2개를 가져야한다.
- 바이너리 힙은 Complete binary tree(완전 이진트리) 속성을 가지고 있다.
- Complete binary tree는 가장 밑의 레벨을 제외하고, preferct binary tree이어야 하고, 가장 밑의 레벨의 노드들은 왼쪽부터 채워져있어야 한다. 그것이 Complete binary tree이다. 그 외는 Complete binary tree가 아니다.
- 중요한 성질은, 모든 엔트리(혹은 노드)가 heap-order property (힙-순서 속성)을 만족해야한다.
- heap-order property는 부모의 key가 자식의 key보다 항상 작아야, 혹은 커야하는 속성을 말한다.
바이너리 힙의 설계
여러가지 방법이 있지만, 예시로, 배열(arrays)를 통해서 설계하는 방법을 알아보겠다.
배열로 설계 할 때, Level-order traversal (트리의 레벨 순서대로 조회)를 이용하여 배열에 저장한다.
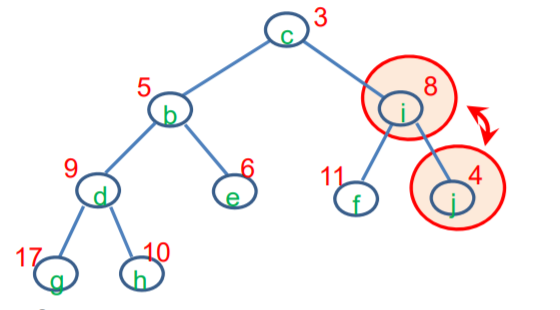
아래의 그림에 보듯이, 배열에 저장되는 순서 1, 2, 3, 4, .. 가 a, b, c, d, ... 순서로 저장되는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이것이 Level-order traversal 순서이다. 즉, 이 순서로 배열에 저장된다.
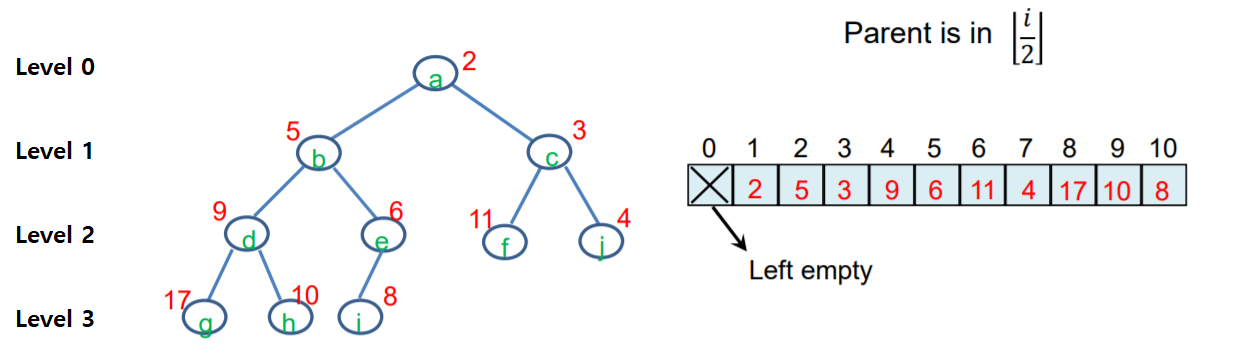
배열(arrays)를 통해서, Level-oder traveral 순서로 설계할 때, 아래의 규칙이 지켜져야한다.
규칙 1. 배열의 0번째는 사용하지 않는다.
규칙 2. i 노드의 자식은 배열의 2i번째, 2i+1번째의 값이 해당된다. ( node[i]의 자식은, node[2i] 그리고 node[2i+1]
규칙 3. 그 말은, noed[i]의 부모는 node[i/2] (소숫점이하 버림)이 되는 것이다.
동작 (Operations)
아래와 같은 동작들이 있다. 요약하면, min, insert, 그리고 removeMin() 이렇게 3개가 있다.
*주의 : 보통 binary 힙에서는 search를 하지않는다.
1. Entry min()
1. 노드 중에서 Root노드를 반환한다
2. Entry insert(key, value)
1. 노드(k, v)를 가진 x가 있다.
2. 이 x는 트리의 가장 낮은 레벨에서, 현재 빈 공간(왼쪽에서부터 차례대로 채워지는)에 위치한다. (배열 인덱스로는 가장 마지막 인덱스가 해당된다)
3. heap-order property를 검사하고, 만족할 때까지 계속 고친다. (자식노드는 부모보드보다 항상 커야한다)
(즉, x의 key와 부모의 key를 비교하여, 그것이 작으면 교환한다. 이것을 property가 만족할 때 까지 반복한다.)


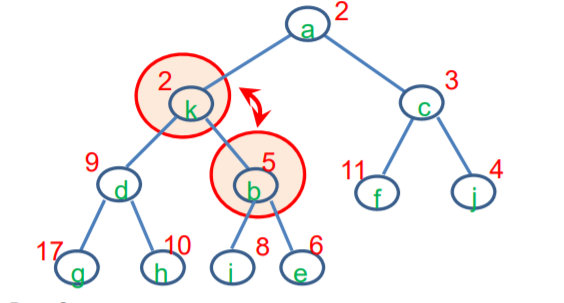
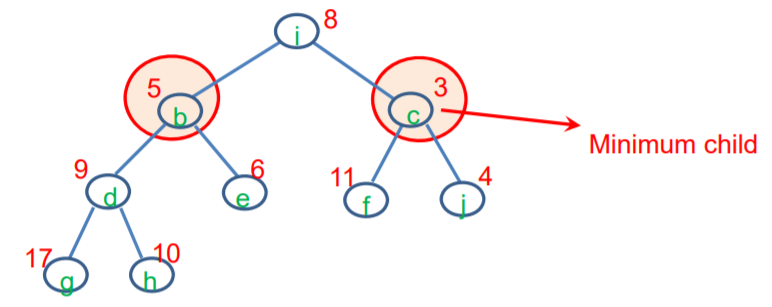
3. Enter removeMin() (혹은 removeMax)
1. 루트 노드를 제거한다.
2. 그 값을 반환한다.
3. 트리의 가장 마지막의 노드를 가져와, 루트노드에 채운다.
4. heap-order property를 검사하고, 만족할 때까지 계속 고친다.
(즉, x가 자식들 중 하나, 혹은 두개의 자식보다 크면, x와 자식들이 가진 값 중 최소 값을 가진 자식과 교환한다. 이것을 property가 만족할때 까지 반복한다.)



복잡도
Complexity
| Searh | Insert | Remove | Max/Min | |
| Array (unsorted) | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Array (sorted) | O(log2n) | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) |
| Linked List | O(n) | O(1) | O(n) | O(n) |
| Binary Heap | O(log2n) | O(log2n) | O(log2n) | O(1) |
코드구현
Java
class MinBinaryHeap {
// Member variables of this class
private int[] Heap;
private int size;
private int maxsize;
// Initializaing front as static with unity
private static final int FRONT = 1;
// Constructor of this class
public MinBinaryHeap(int maxsize) {
// This keyword refers to current object itself
this.maxsize = maxsize;
this.size = 0;
Heap = new int[this.maxsize + 1];
Heap[0] = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
// Method 1
// Returning the position of
// the parent for the node currently
// at pos
private int parent(int pos) { return pos / 2; }
// Method 2
// Returning the position of the
// left child for the node currently at pos
private int leftChild(int pos) { return (2 * pos); }
// Method 3
// Returning the position of
// the right child for the node currently
// at pos
private int rightChild(int pos) {
return (2 * pos) + 1;
}
// Method 4
// Returning true if the passed
// node is a leaf node
private boolean isLeaf(int pos) {
if (pos > (size / 2) && pos <= size) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Method 5
// To swap two nodes of the heap
private void swap(int fpos, int spos) {
int tmp;
tmp = Heap[fpos];
Heap[fpos] = Heap[spos];
Heap[spos] = tmp;
}
// Method 6
// To heapify the node at pos
private void minHeapify(int pos) {
// If the node is a non-leaf node and greater
// than any of its child
if (!isLeaf(pos)) {
if (Heap[pos] > Heap[leftChild(pos)]
|| Heap[pos] > Heap[rightChild(pos)]) {
// Swap with the left child and heapify
// the left child
if (Heap[leftChild(pos)]
< Heap[rightChild(pos)]) {
swap(pos, leftChild(pos));
minHeapify(leftChild(pos));
}
// Swap with the right child and heapify
// the right child
else {
swap(pos, rightChild(pos));
minHeapify(rightChild(pos));
}
}
}
}
// Method 7
// To insert a node into the heap
public void insert(int element) {
if (size >= maxsize) {
return;
}
Heap[++size] = element;
int current = size;
while (Heap[current] < Heap[parent(current)]) {
swap(current, parent(current));
current = parent(current);
}
}
// Method 7
// To remove and return the minimum
// element from the heap
public int remove() {
int popped = Heap[FRONT];
Heap[FRONT] = Heap[size--];
minHeapify(FRONT);
return popped;
}
// Method 9
// To return the minimum
// element from the heap at root
public int min() {
return Heap[FRONT];
}
// Method 10
// To print the contents of the heap
public void print() {
for (int i = 1; i <= size / 2; i++) {
// Printing the parent and both childrens
System.out.print(
" PARENT : " + Heap[i]
+ " LEFT CHILD : " + Heap[2 * i]
+ " RIGHT CHILD :" + Heap[2 * i + 1]);
// By here new line is required
System.out.println();
}
}
}
public class binary_heap_test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Display message
System.out.println("The Min Heap is ");
// Creating object opf class in main() methodn
MinBinaryHeap minHeap = new MinBinaryHeap(15);
// Inserting element to minHeap
// using insert() method
// Custom input entries
minHeap.insert(5);
minHeap.insert(3);
minHeap.insert(17);
minHeap.insert(10);
minHeap.insert(84);
minHeap.insert(19);
minHeap.insert(6);
minHeap.insert(22);
minHeap.insert(9);
// Print all elements of the heap
minHeap.print();
// Removing minimum value from above heap
// and printing it
System.out.println("The Min val is " + minHeap.remove());
}
}출력결과
| The Min Heap is PARENT : 3 LEFT CHILD : 5 RIGHT CHILD :6 PARENT : 5 LEFT CHILD : 9 RIGHT CHILD :84 PARENT : 6 LEFT CHILD : 19 RIGHT CHILD :17 PARENT : 9 LEFT CHILD : 22 RIGHT CHILD :10 The Min val is 3 |
인용/참고자료
한양대학교 - 데이터 구조론 (우선순위 큐)
http://www.kocw.net/home/cview.do?cid=ec066a0f24e13e9a
GeeksforGeeks - MinHeap implementation
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/min-heap-in-java/
도움이 되셨으면 "공감"버튼을 눌러주실 수 있을까요?
더 많은 도움을 드리는 게시글을 작성하겠습니다.
'자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [자료구조] 큐(Queue) (0) | 2022.11.27 |
|---|---|
| [자료구조] 이중 연결 리스트 (더블 링크드 리스트) C/C++ (0) | 2022.05.13 |
| [자료구조] 세그먼트 트리, 쉽게 이해하기 (0) | 2022.01.19 |
| [자료구조](작성중) 추상 데이터 타입과 자료구조의 차이점 (0) | 2021.10.17 |
| (작성중) [자료구조] 우선순위 큐란? (Priority Queue) (0) | 2021.10.17 |